
Citric Acid Cycle Enzymes Mnemonic Tutorial (3/5) Citrate Synthase
If ATP is needed: Citric acid cycle If ATP is sufficient: Fatty acid synthesis Steps where ATP is generated in Kreb's Cycle PDH includes cofactors and conenzymes. Easy way to remember this is - they are vitamin B or vitamin B like: Vitamin B1 - Thiamine (Thiamine Pyrophosphate/TPP) for PDH (E1)
5.3 The Citric Acid Cycle Introductory Biochemistry
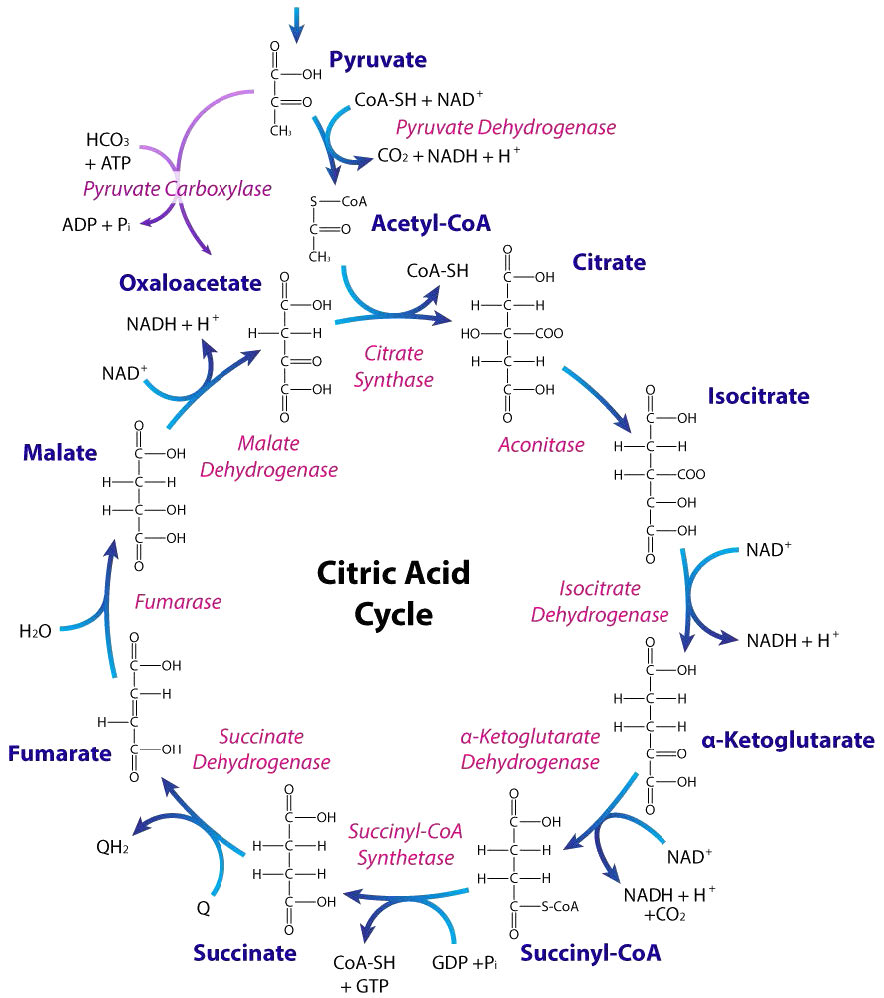
The citric acid cycle captures the energy stored in the chemical bonds of acetyl CoA (processed glucose) in a step-by-step process, trapping it in the form of high-energy intermediate molecules. The trapped energy from the citric acid cycle is then passed on to oxidative phosphorylation, where it is converted to a usable form of cellular energy, ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
The Citric Acid Cycle The Catabolism of AcetylCoA Basicmedical Key
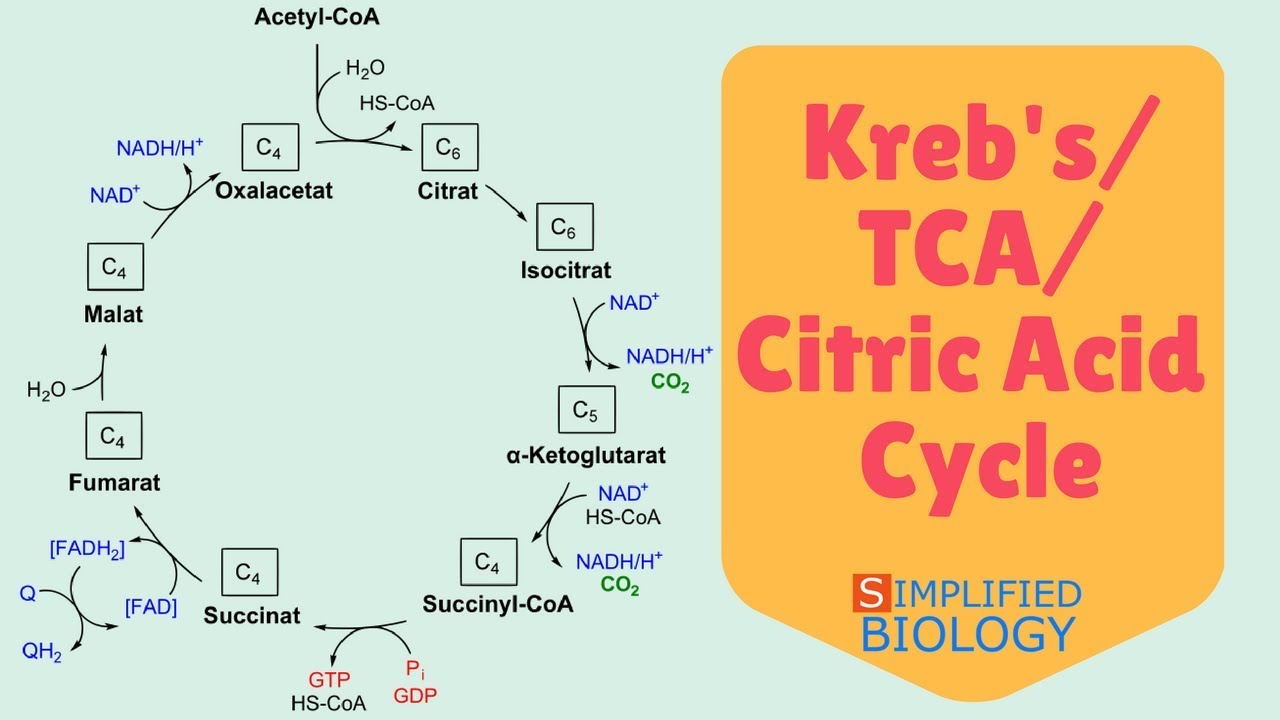
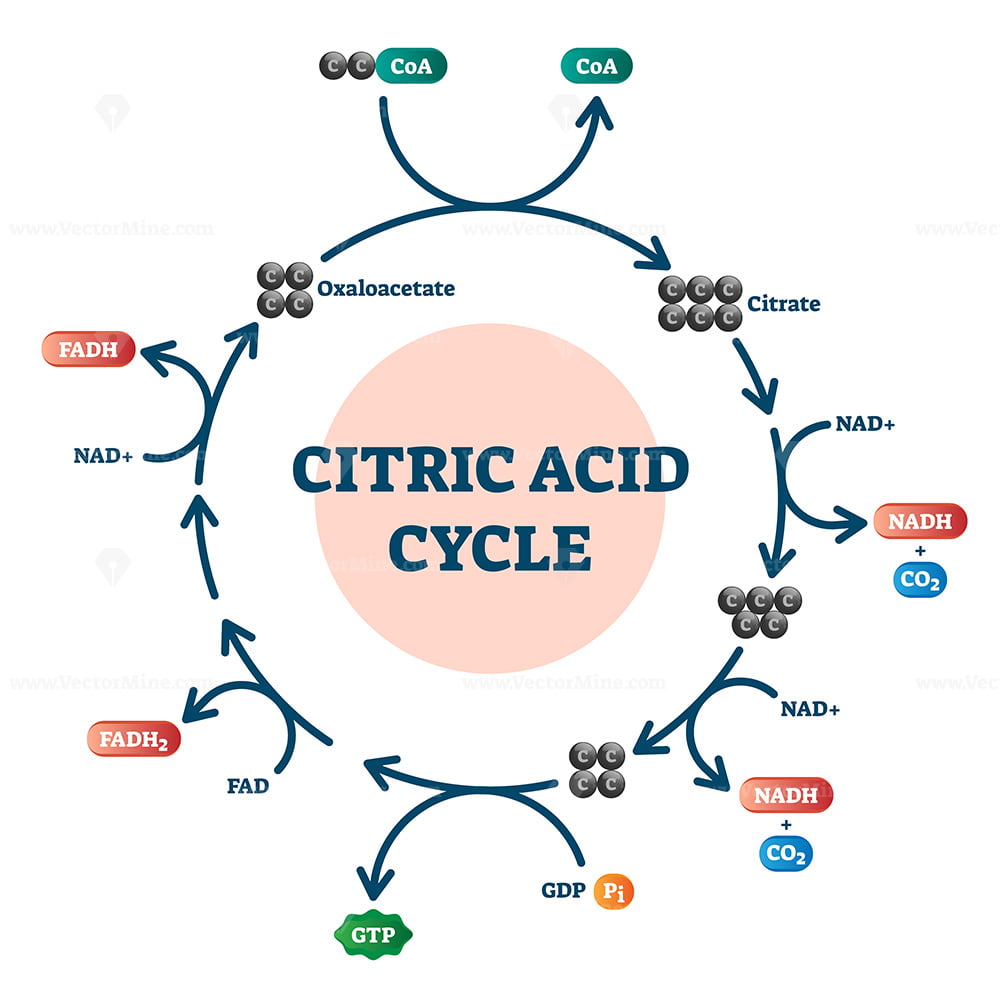
Chemist Notes September 2, 2023 Metabolism Table of Contents Citric acid cycle or TCA cycle or Kreb's cycle Steps and reactions of the citric acid cycle 1) Formation of citrate 2) Formation of isocitrate via cis-aconitate 3) Oxidation of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate and CO2 4) Oxidation of α-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA and CO2
[Short Trick] Krebs Cycle Citric acid cycle Learn Quick by Mnemonics
Citric acid cycle Pentose phosphate pathway Electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation Gluconeogenesis Glycogen metabolism Glycolysis Osmosis Carbohydrate Metabolism high-yield notes offers clear overviews with striking illustrations, tables, and diagrams. Make learning more manageable.

Sitronsyresyklus Citric acid cycle xcv.wiki
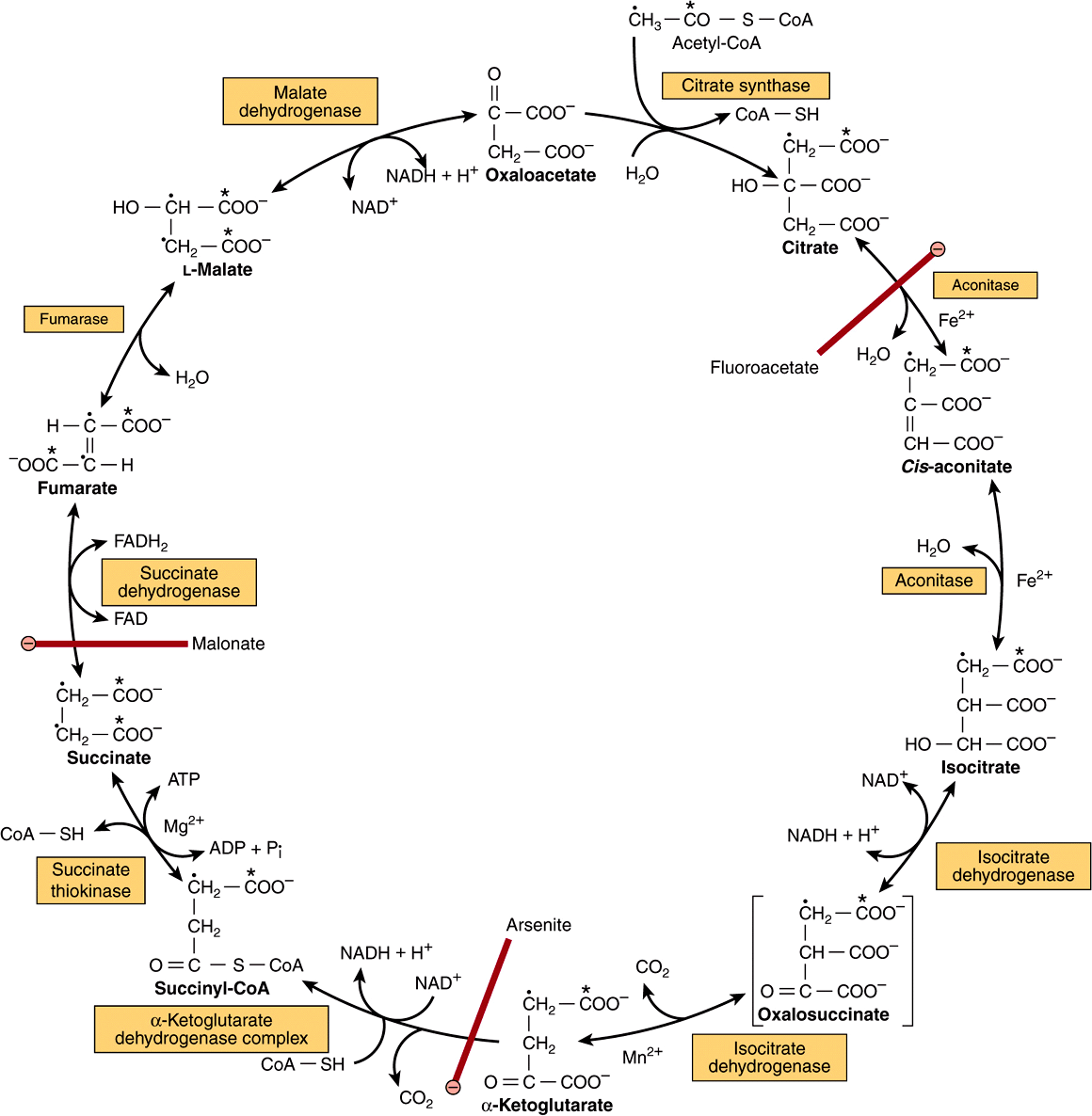
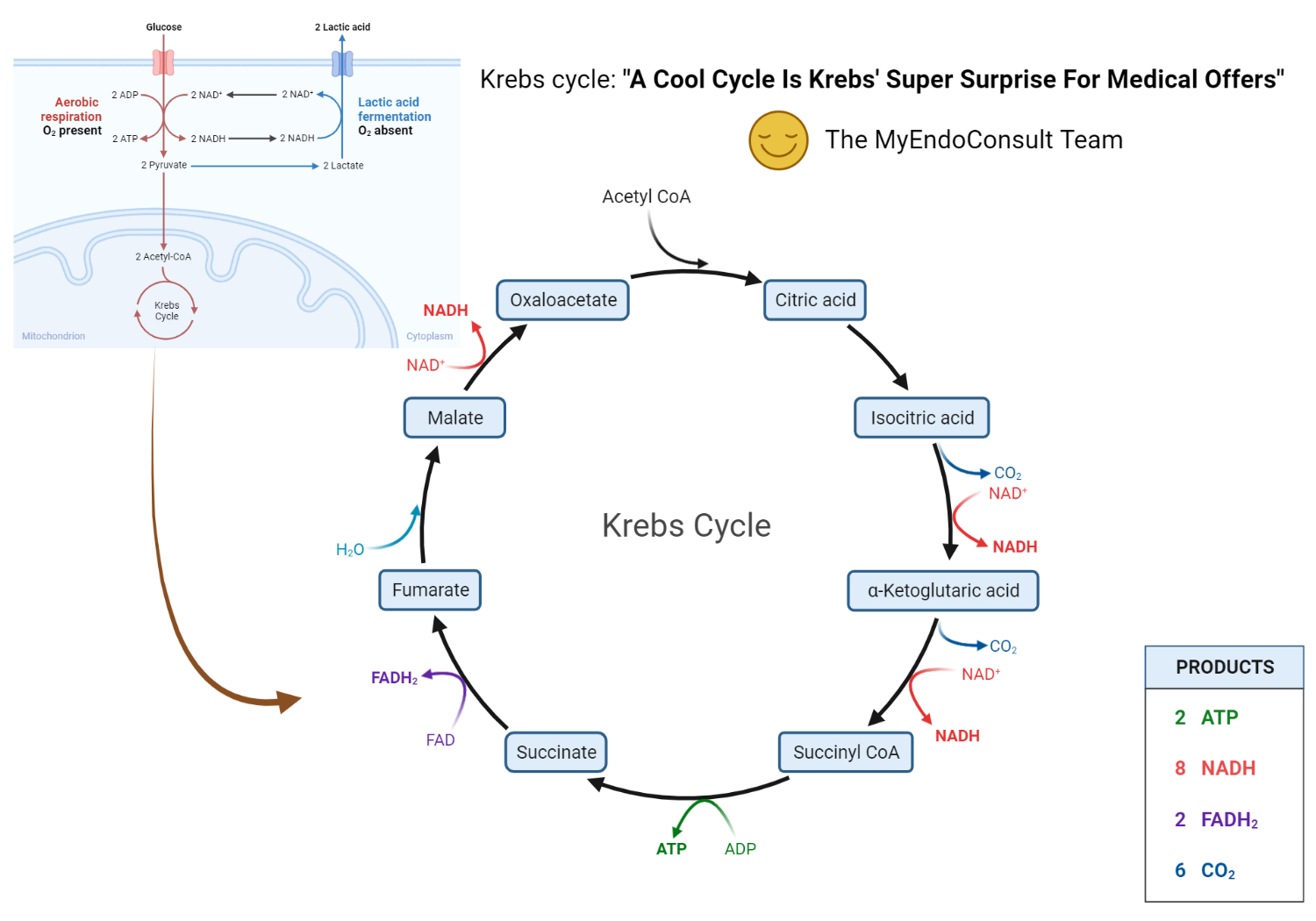
Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle or Tricarboxylic acid cycle. The Krebs cycle occurs in mitochondria and all the enzymes are present in the mitochondrial matrix, either free or attached to the inner mitochondrial membrane and the cristae membrane.

Krebs Cycle/ TCA Cycle Mnemonic Simplified Biology
Now let's outline the steps of the Krebs cycle: Acetyl-CoA (2 carbons) combines with oxaloacetate (4 carbons) to form citrate (6 carbons). This reaction is catalyzed by citrate synthase. Citrate is converted to cis-aconitate, and then to isocitrate by aconitase, involving a dehydration and hydration step.
Memorize The Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) With Easy Mnemonics
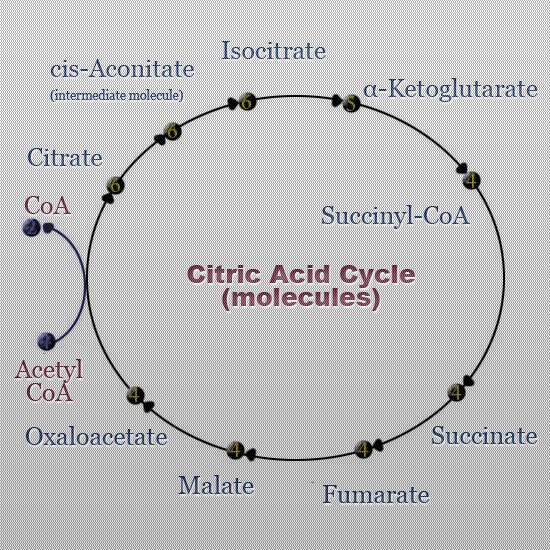
Isocitrate (K) Keep Alpha-Ketoglutarate (SC) Selling Succinyl-CoA (SU) Substances Succinate (F) For Fumarate (M) Money Malate (O) Officer Oxaloacetate Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like (C) Can, (I) I, (K) Keep and more.

The Citric Acid Cycle Diagram Quizlet
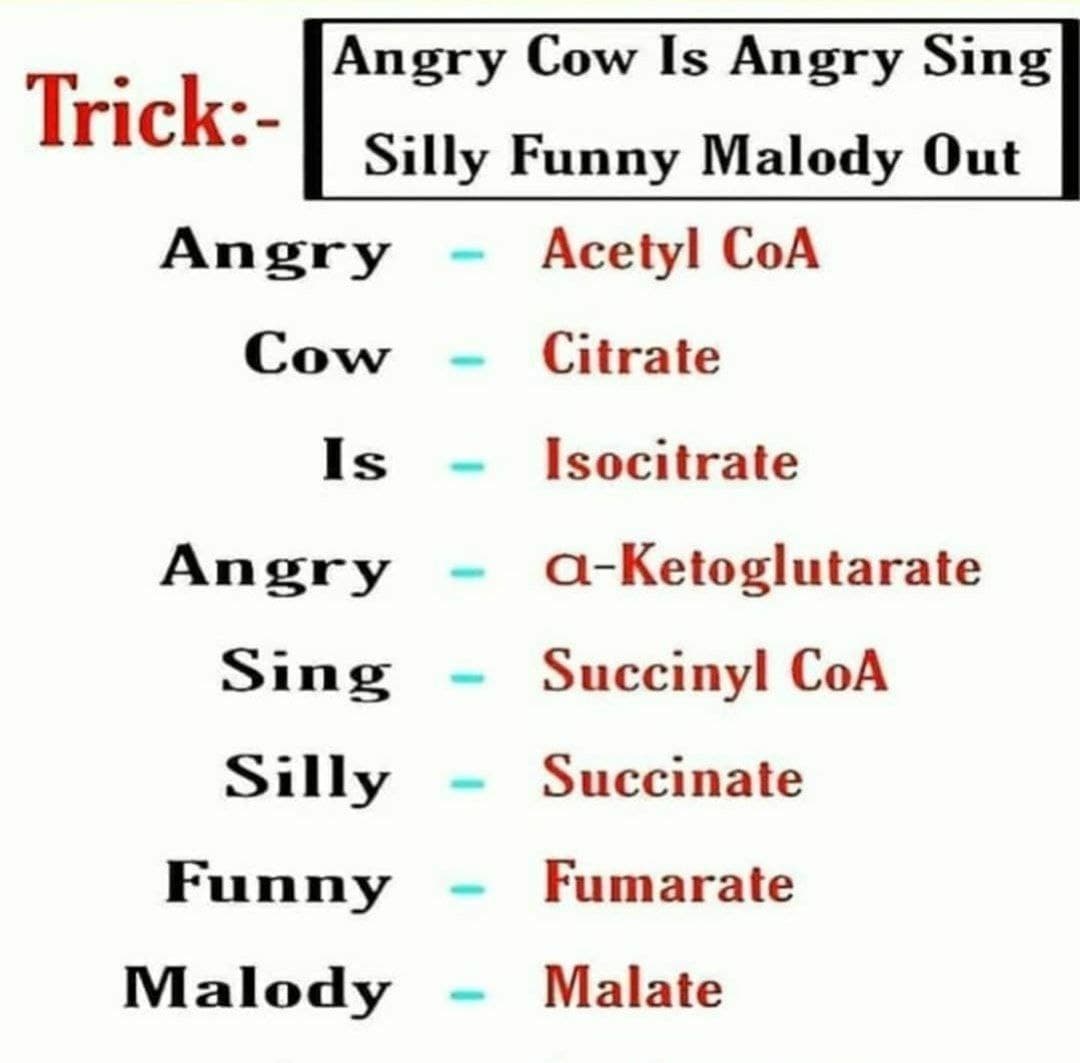
0 Citric Acid Cycle - Mnemonic Oh Citric Acid Is Ofcourse A Silly Stupid Funny Molecule O xaloacetate C itrate A conitate I socitrate O xalosuccinate A lpha ketoglutarate S uccinyl CoA S uccinate F umarate M alate NOTE: (SiLly & sTupid helps to differentiate succinLy coA & succinaTe)
CITRIC ACID/ KREBS/ TCA CYCLE with Mnemonic for NEET, AIIMS, AIPMT
The citric acid cycle is a closed loop; the last part of the pathway reforms the molecule used in the first step. The cycle includes eight major steps. In the first step of the cycle, acetyl CoA combines with a four-carbon acceptor molecule, oxaloacetate, to form a six-carbon molecule called citrate.
Citric acid cycle diagram, vector illustration molecular scheme
Citric Acid Cycle Mnemonic (B: 2/5): Biochem Tutorial: Krebs cycle, substrates, citrate, isocitrate HelpHippo 28.1K subscribers Subscribe 35K views 9 years ago More tutorials and flashcards at.

8 Steps of Citric acid Cycle (Krebs cycle) and Enzymes involved in each
Citric Acid Enzymes: S imps (Citrate S ynthase) A sk ( A conitase) D umb (Isocitrate D ehydrogenase) D aughters (A-ketoglutarate D ehydrogenase) S ucking (Succinyl-CoA S ynthase) D *ck (Succinic D ehydrogenase) F or ( F umerase) D rinks (Malate D ehydrogenase) All of the S's are short for synthase and all of the D's are short for dehydrogenase.
Krebs Cycle Mnemonic My Endo Consult
Mnemonic Connecting Citric Acid Cycle & ETC I've been working on a way to remember all the details and interactions between TCA Cycle and ETC (enzymes, energy carriers, structures etc.) and found this to be helpful for me. Let's start with the basics to get down before going into the story.

Citric Acid Cycle Mnemonic (B 2/5) Biochem Tutorial Krebs cycle
What is alpha-Ketoglutarate made from? Reaction 1. Which TCA reaction? High Bond energy in Acetyl-CoA (makes up for low OAA concentrations) What fuels TCA Reaction 1? Citrate. What is the product of TCA Reaction 1? Citrate Synthase. What is the enzyme of TCA Reaction 1?

Regulation Of The Cycle Citric Acid Cycle MCAT Content
The citric acid cycle - also known as the TCA cycle or the Krebs cycle - is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored en.

Citric Acid (Kreb's) Cycle steps Mnemonic Biochemistry Mnemonic YouTube
The Krebs cycle - also called the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle - is the first step in the aerobic pathway, and it operates to continually synthesize enough of a substance called oxaloacetate to keep the cycle going, although, as you'll see, this is not really the cycle's "mission."

Krebs cycle / Citric acid cycle / TCA cycle & ATP count Mnemonic series
Picmonic. The citric acid cycle, also called the Krebs cycle, is an important biochemical reaction used by aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl co-enzyme A. Each cycle takes in an acetyl-CoA, which comes from the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, and goes through a series of oxidation.