
Examples Of Longitudinal Waves page2 / Generally, waves moving
Course: Oscillations and waves (Essentials) - Class 11th > Unit 3. Lesson 1: Introduction to waves. Introduction to waves. Identifying transverse and longitudinal waves. Transverse and longitudinal waves review. Science >. Oscillations and waves (Essentials) - Class 11th >. How do we know that the universe is expanding? >.
PPT Properties of Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
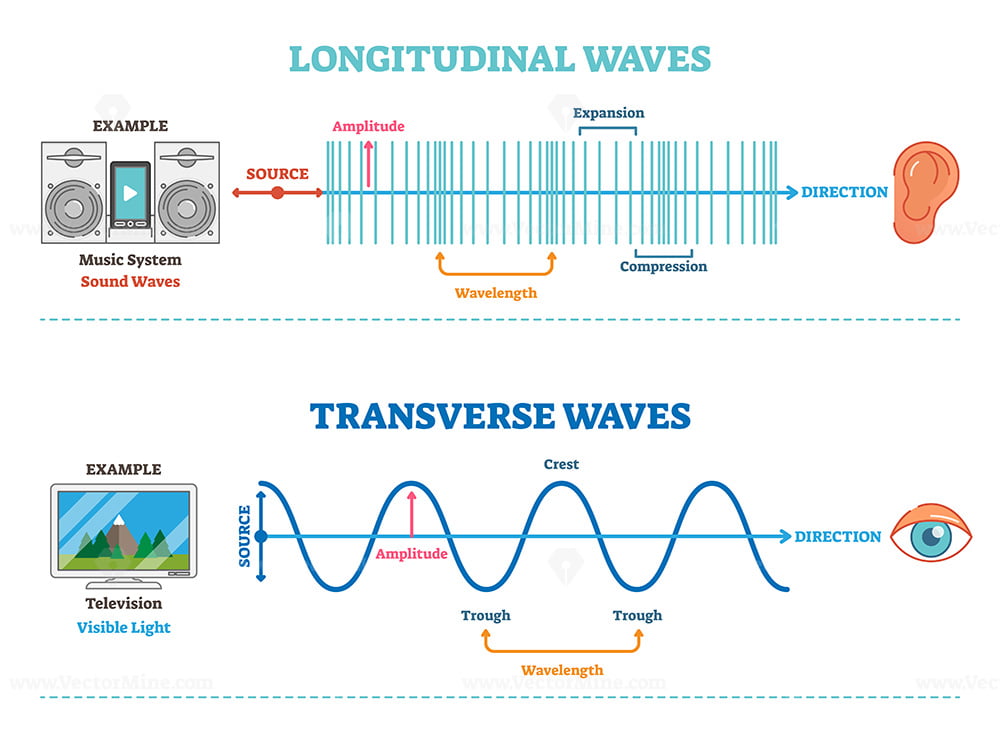
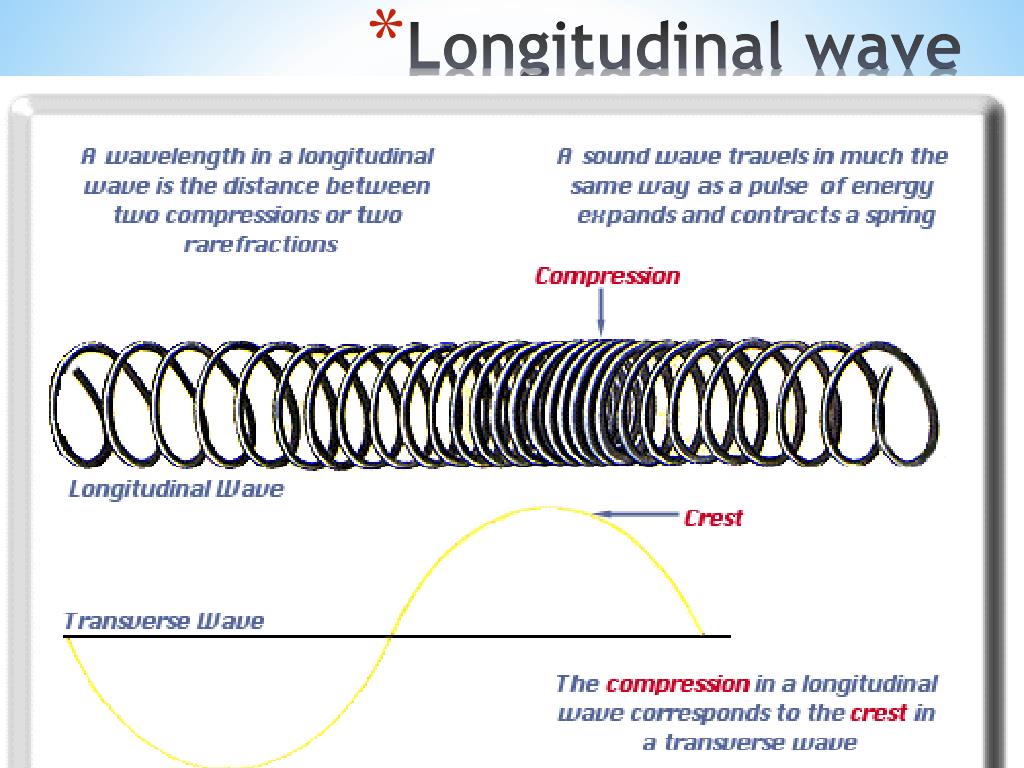
Longitudinal and transverse waves. Diagram illustrating longitudinal and transverse waves. The high points of the transverse waves (peaks) represent more-dense areas of the longitudinal waves, and the low points (troughs) represent less-dense areas. The arrows show the directions of wave material movement.

Properties of waves and wave cycles. Scalar, transverse, energy and
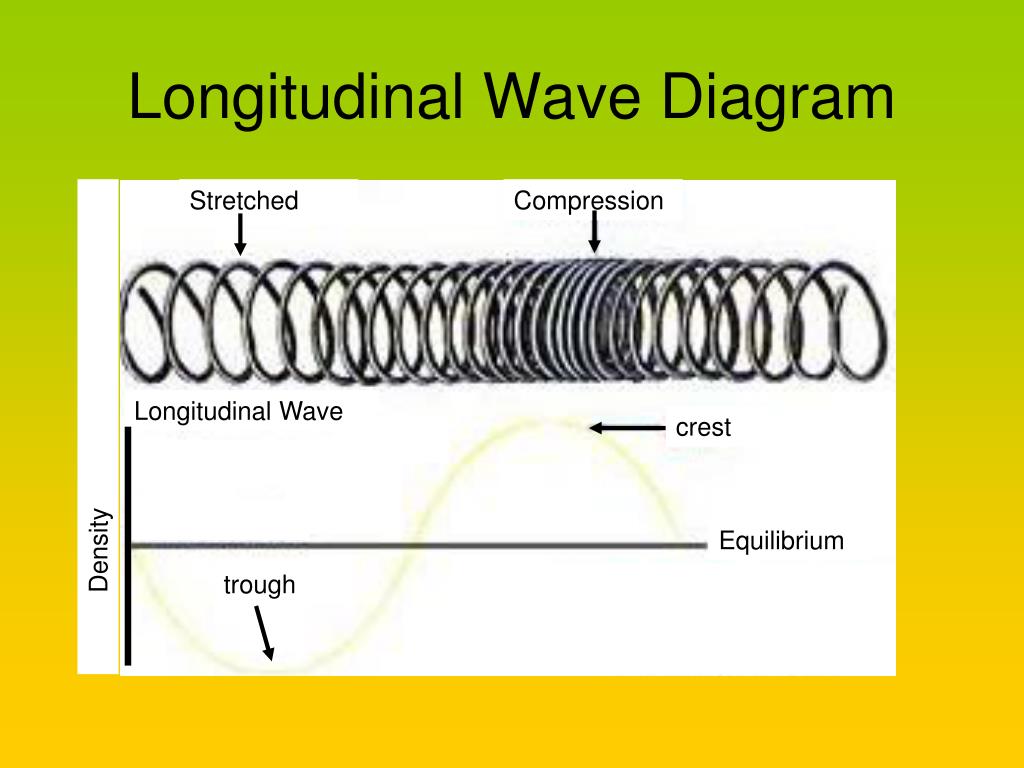
A longitudinal wave is a type of mechanical wave, or wave that travels through matter, called the medium. In a longitudinal wave, particles of the medium vibrate in a direction that is parallel to the direction that the wave travels. Places where particles of the medium crowd closer together are called compressions.
PPT Chapter 17 Mechanical Waves & Sound PowerPoint Presentation ID
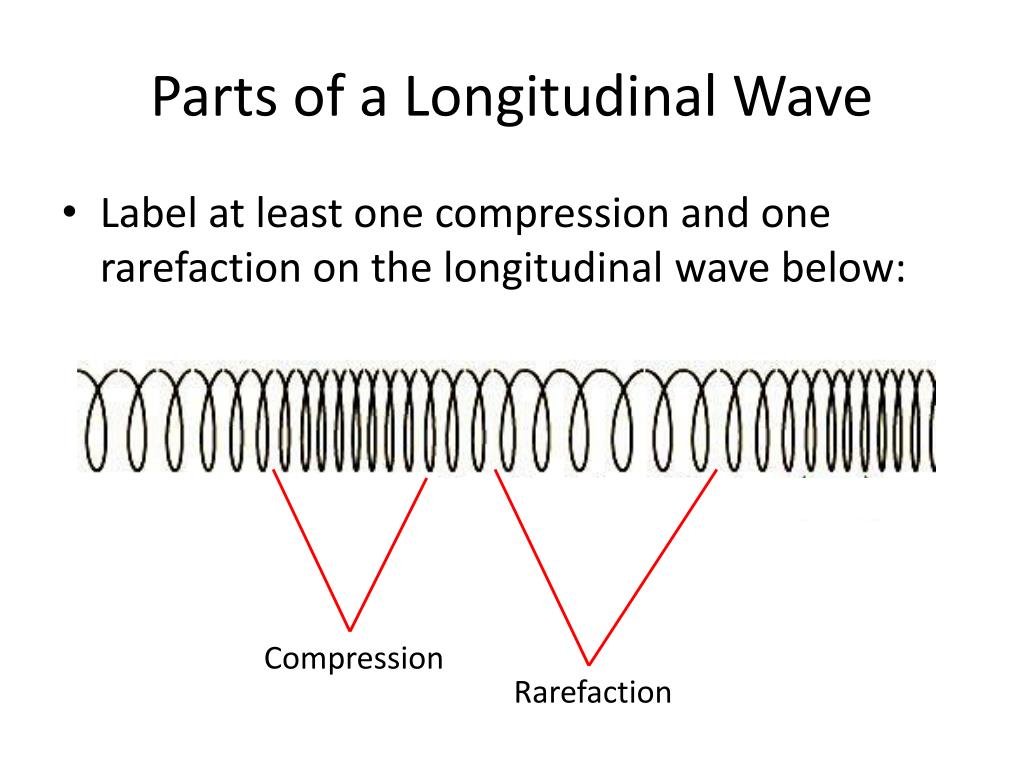
Longitudinal waves are waves where the displacement of the medium is in the same direction as the direction of the travelling wave. The distance between the centres of two consecutive regions of compression or the rarefaction is defined by wavelength, λ.
Types of longitudinal, transverse and surface waves examples outline
1.6: Longitudinal Waves. In comparing simulations on transverse waves (Tutorial 1.3) with vertical harmonic motion (Tutorial 1.4) we discovered that particles in a transverse wave move up with simple harmonic motion. In the previous exercise (Tutorial 1.5) we saw that harmonic motion can also occur in the horizontal direction.
[Solved] Draw a longitudinal wave and label the following properties
rarefaction longitudinal wave, wave consisting of a periodic disturbance or vibration that takes place in the same direction as the advance of the wave.

6 Illustration of a transverse wave and a longitudinal wave Download
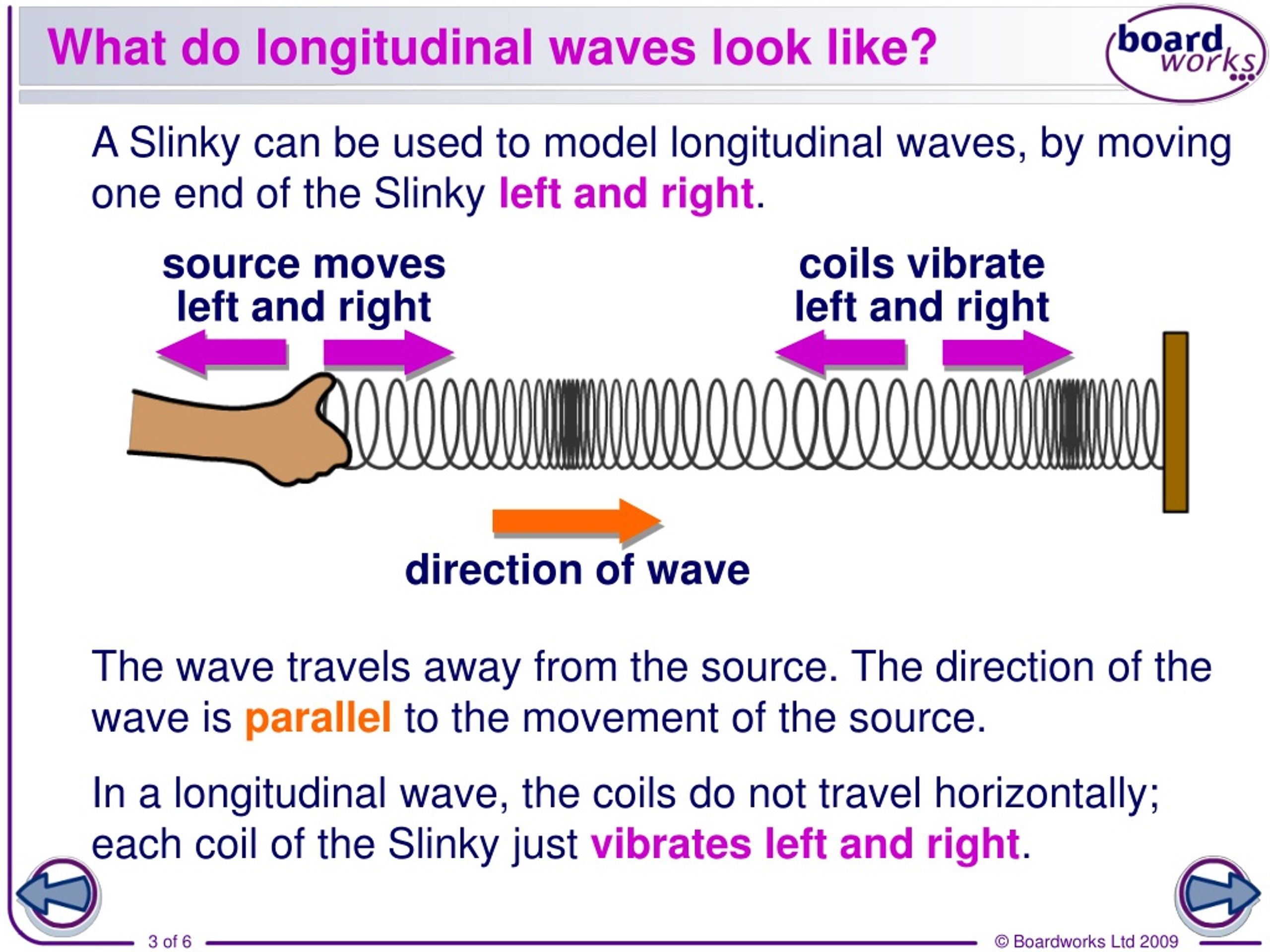
A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium are displaced in a direction parallel to the direction of energy transport. A longitudinal wave can be created in a slinky if the slinky is stretched out horizontally and the end coil is vibrated back-and-forth in a horizontal direction.

GCSE Physics Longitudinal and Transverse Waves YouTube
166 longitudinal and transverse waves stock photos, 3D objects, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See longitudinal and transverse waves stock video clips Filters All images Photos Vectors Illustrations 3D Objects Sort by Popular Properties of Wave cycles physics. spring stretched. transverse waves. longitudinal.

Longitudinal Wave Photograph by Science Photo Library
434 longitudinal wave stock photos, 3D objects, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See longitudinal wave stock video clips Filters All images Photos Vectors Illustrations 3D Objects Sort by Popular Sound propagates as density or pressure variations, Reflection of sound, tuning fork sound propagation
Longitudinal Wave Anatomy ANATOMY STRUCTURE
End of image gallery. In the diagram, the compressions move from left to right and energy is transferred from left to right. However, none of the particles are transported along a longitudinal wave.

Longitudinal Wave เวกเตอร์สต็อก (ปลอดค่าลิขสิทธิ์) 211513915
of 1 Browse Getty Images' premium collection of high-quality, authentic Longitudinal Wave stock photos, royalty-free images, and pictures. Longitudinal Wave stock photos are available in a variety of sizes and formats to fit your needs.

Longitudinal wave Stock Image F012/2823 Science Photo Library
Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation.
PPT What are longitudinal waves? PowerPoint Presentation, free
Unlike transverse waves, longitudinal waves cause the particles of medium to move parallel to the direction of the wave. They are most common in springs, where they are caused by the pushing an pulling of the spring. As shown in the image below, longitudinal waves are a series of compressions and rarefactions, or expansions. The wavelength of.

Schematic diagram of a sound (longitudinal) wave produced by a
One way to remember the movement of particles in longitudinal waves is to use the 'P' sound:. End of image gallery. In the diagram, the compressions move from left to right and energy is.

Characteristics Of Longitudinal And Transverse Waves Class 11
In longitudinal (or compression) waves the displacement is along the axis of propagation. RM AXNNDG - Mechanical device for demonstrating longitudinal waves RF D312NG - Diagram showing transverse and longitudinal wave forms. RF 2RBKPGD - Parts of a wave Crest, trough, wavelength, and amplitude. vector illustration
PPT Chapter 11 Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1901329
In a longitudinal wave the particles are displaced parallel to the direction the wave travels. An example of longitudinal waves is compressions moving along a slinky. We can make a horizontal longitudinal wave by pushing and pulling the slinky horizontally.